1. About
Quantified Uncertainty with Optimization for the Finite Element Method (quoFEM) is an open-source research application, that is hosted on the quoFEM Github page, and released under the 2-Clause BSD license (see Copyright and License). The application provides uncertainty quantification methods (forward, inverse, reliability, sensitivity, parameter estimation, and surrogate modeling) to researchers in natural hazards who utilize existing simulation software applications, such as Finite Element applications, in their research. It has been developed at the SimCenter, within the University of California, Berkeley. The SimCenter is part of the Natural Hazards Engineering Research Infrastructure (NHERI) program, funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
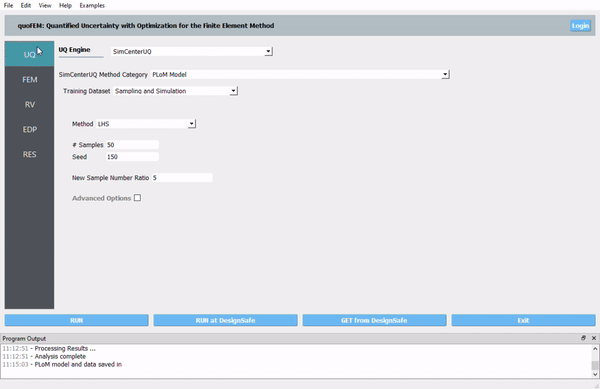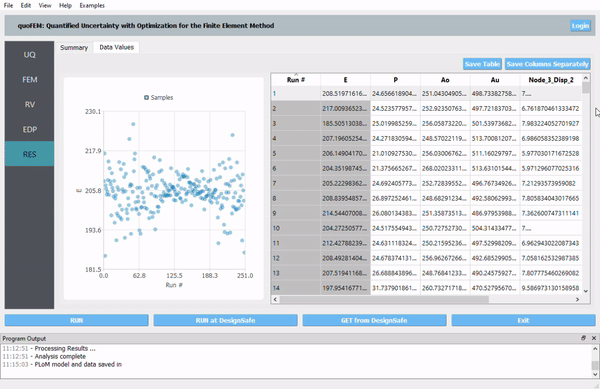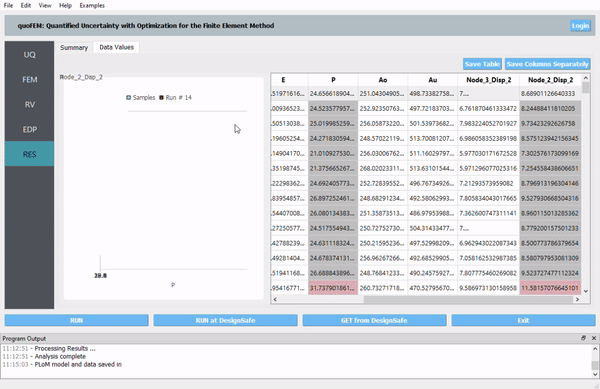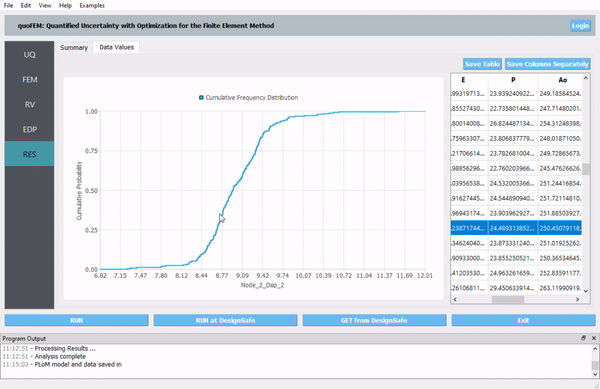
Fig. 1.1 quoFEM
Depending on the type of numerical simulation being performed, the additional simulation required for uncertainty quantification can be computationally prohibitively expensive. To overcome this impediment, the user has the option to perform the response simulations on the Frontera supercomputer. Frontera is located at the Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) and made available to the user through NHERI DesignSafe-CI, the cyberinfrastructure provider for the distributed NSF-funded Natural Hazards Engineering Research Infrastructure (NHERI) facility.
This is Version 4.1 of the tool. Users are encouraged to comment on what additional features and capabilities they would like to see in this application. These requests and feedback can be submitted through an anonymous user survey. We greatly appreciate any input you have. If there are features you want, chances are many of your colleagues also would benefit from them. Users are encouraged to review the Requirements to see what features are planned for this application.
1.1. Capabilities and Limitations
Below are key capabilities and limitations of quoFEM, categorized by Uncertainty Quantification (UQ), Finite Element Method (FEM), Random Variables (RV), Quantity of Interest (QoI), Results (RES), and general.
Item |
Capabilities |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|
UQ |
Easy access to different UQ methods. Parallelized UQ algorithms. Multiple alternative algorithms for each method. |
No support for optimization under uncertainty and local sensitivity analysis. |
FEM |
Easy interface for user-provided simulation models (not only FEM models but any model), including Opensees, python, or any other simulation models (e.g. FEM or non-FEM software) with a python-scripted interface. |
No support to assist modeling, e.g. creation of hazards and structural models. Those are featured in other tools of SimCenter. |
RV |
12 different kinds of probability distributions with correlations. |
No support for random fields, non-Gaussian copular, or user-defined variables. |
QoI |
Scalar and vector QoI. Parsing of QoI names using a post-processing script. |
|
RES |
Interactive plotting of scatter charts, histograms, and cumulative mass functions. Summary of statistics. Save data into a CSV file. |
Limited flexibility in visualization. |
General |
Graphical user interface. Free and easy one-click remote running option. |